What is Inappropriate Foreign Influence?
The term “foreign influence” has been coined by various federal agencies, but there is no consistent definition. Generally, the term refers to a set of actions carried out by a foreign entity against a U.S. party/parties, by which the foreign party positions itself to obtain a benefit not intended for it (potentially by illegal means). “Foreign influence” is often used to illegally obtain U.S. intellectual property and technology, compromise U.S. computer systems, and/or affect the course of U.S. research to benefit the foreign instigator(s).
Since 2018, Federal agencies have significantly increased their investigative focus on U.S. universities in response to Congressional concerns that misappropriation of sensitive IP and acquisition of certain emerging technologies potentially compromises national security.
Federal concerns fall into four main areas, which affect primary institutional functions:
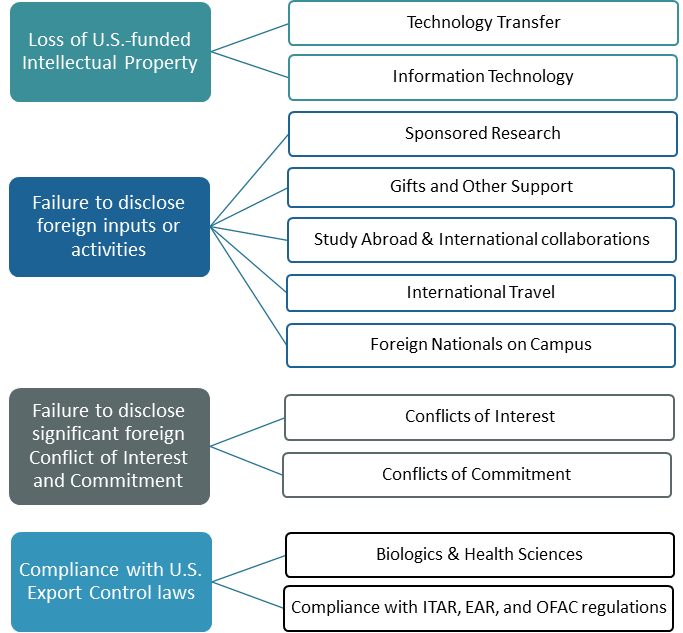
In response to bipartisan, growing federal concern, many agencies have issued guidance documents and/or new requirements relating to identifying inappropriate foreign influence. Please see ORED’s “ Guidance Regarding Foreign Influence and Research ” for more information on Sponsor notifications and reporting requirements.